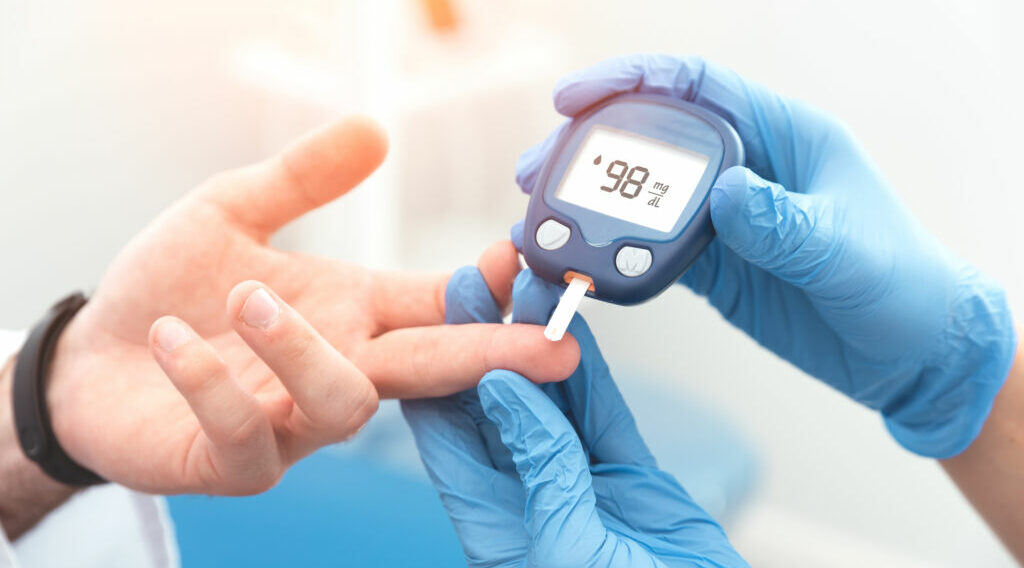
People who have a parent or two parents with type-2 diabetes are at an increased risk of getting the disease as well. With both parental genes, there is about five times more likely than average for your child to develop this chronic illness if they inherit just one copy from each parent. BGS Gleneagles Global Hospital houses one of the best endocrinologists in Bangalore who specializes in treating all types of diabetes.
Diabetes is a complex condition with several types and no clear cause. However, there are risks to genetics when it comes to developing diabetes; some people may inherit the gene that causes the problem while others can develop type 2 through environmental factors like diet or lifestyle choices they make which then influences their chances of passing this on down generations too.
One known risk factor for developing the disease includes a person’s family history, but there are also many other factors that can lead to this chronic illness like obesity and poor diet choices
The general symptoms of diabetes include:
- Increased hunger
- Thirst and frequent urination.
- Many people also experience weight loss
Blurry vision due to lack of eye glucose (sugar) which can lead to blindness if left untreated or uncontrolled for too long by medication like insulin injections that help regulate sugar levels in the body.
- Extreme fatigue as well as sores that don’t heal because they’re diabetic foot ulcers An open sore on your skin caused by poor circulation stemming from high blood sugars instead used proper footwear when doing physical activities.
No type of diabetes mellitus is genetic per se, but your DNA may influence how it reacts to an environmental trigger.
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disease that occurs when the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks healthy cells. It can develop at any age but usually appear during adolescence or young adulthood due to certain genetic features making it more likely for this form of glucose intolerance than others with different gene profiles.
Scientists have discovered changes in specific proteins made by genes which could contribute some risk factors towards developing Type-1 DM under certain circumstances where there are environmental stressors present such as infection from viruses like rubella leading us into thinking incorrectly they were causing damage instead because these particular types don’t produce enough antibodies against them.
These proteins play a key role in the immune system. When people are genetically predisposed to certain units, they can trigger type 1 diabetes by factors like infection or injury; once developed, these conditions will last forever unless treated with insulin injections ongoing.
With type 2 diabetes, people are more likely to have a close family member with the condition. Genetic factors may also play some role in who’s susceptible but lifestyle choices such as diet and exercise account for much of one’s risk level when it comes down to these types of chronic illnesses. Other factors that can increase chances include:
- Age 45 years or older; excess weight (high BMI/obesity),
- High body mass index (BMI) relative to height squared divided by height cubed ratio.
- A sedentary lifestyle involving limited physical activity high levels of fat and cholesterol in the blood
- Hypertension
- Polycystic ovary syndrome, which many call PCOS
- History of gestational diabetes, which occurs during pregnancy
- History of cardiovascular disease depression.
Main causes which increase the risk of developing diabetes. They include the following:
- Genes: Certain genes are known to increase the risk of diabetes. The genetic risk is not 100% but is on average between 2050%.
- Family history: A family history of diabetes is a significant risk factor for other family members to develop diabetes.
- Genetic disorders: People born with genetic diseases, such as hemochromatosis (excess iron in the body) and cystic fibrosis, can develop damage to the pancreas, which eventually leads to diabetes.
- Gestational diabetes: In general, a small number of women can develop diabetes during pregnancy.
- Aging with age, the risk of developing type 2 diabetes increases.
- Obesity is now known to be a common risk factor for type 2 diabetes.
- Unhealthy diet: Unhealthy diet is quickly becoming a cause of type 2 diabetes.
- Sedentary lifestyle: people who do not exercise are at greater risk of developing diabetes.
- Hormonal causes: Some very rare hormonal conditions can also lead to type 2 diabetes.
- Medications: Drugs: Certain drugs, such as antipsychotics, are known to cause type 2 diabetes.
Science has confirmed that diabetes is a non-communicable disease, so it’s not contagious and the person cannot get the illness from someone else.
In some cultures, people who have Type 1 or 2 diabetes might be suspected of being infected with the disease from person-to-person contact. Science has confirmed that this isn’t true but it can be heritable. The chance of someone becoming diabetic in the future can increase if their parents are also diagnosed with the condition.